What is a flux core welder used for….?
In the dynamic world of welding, various techniques and tools have emerged to meet the demands of different projects. One such tool that has gained immense popularity is the flux core welder. This versatile welding method offers unique advantages, making it a preferred choice for many professionals and DIY enthusiasts. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of flux core welding, exploring its applications, benefits, and how it stands out in the realm of metal joining.
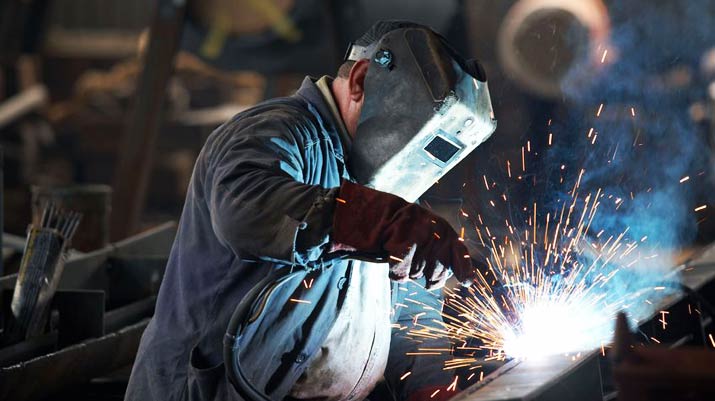

Understanding Flux Core Welding:
Flux core welding, also known as FCAW (Flux Core Arc Welding), is a welding process that utilizes a tubular wire electrode with a flux-filled core. The flux serves multiple purposes during the welding process. It not only shields the molten metal from atmospheric contaminants but also facilitates the creation of a slag that protects the weld bead as it cools. This dual-action mechanism makes flux core welding a highly efficient and practical method for various applications.
Applications of Flux Core Welding:
1. Construction Industry:
Flux core welding finds extensive use in the construction industry, where its high deposition rates and deep penetration capabilities are highly valued. From welding structural steel beams to fabricating components for bridges and buildings, flux core welding proves to be a reliable and efficient choice.
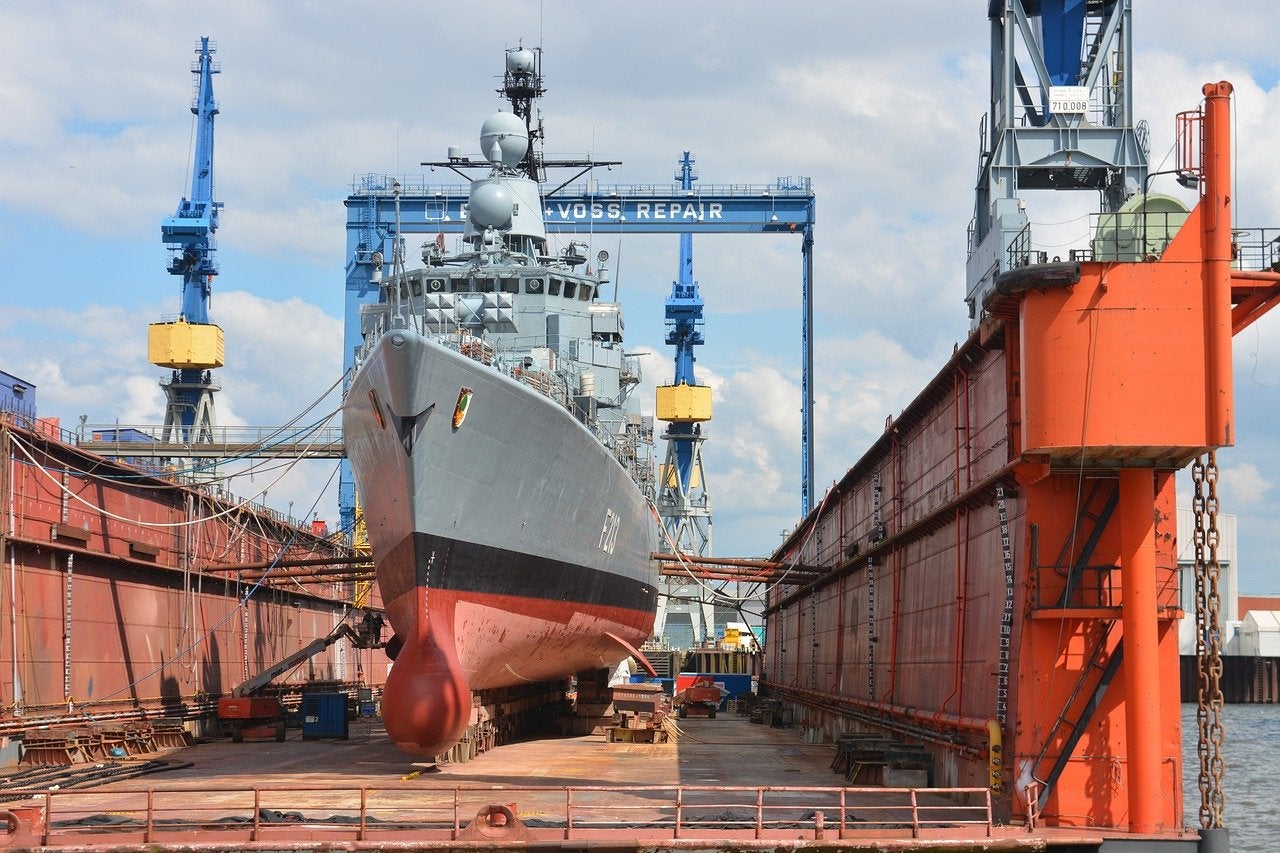
2. Shipbuilding:
The maritime industry relies on flux core welding for its ability to produce strong and durable welds in a variety of positions. Whether it’s joining steel plates for ship hulls or fabricating intricate components for marine structures, flux core welding plays a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity of maritime constructions.

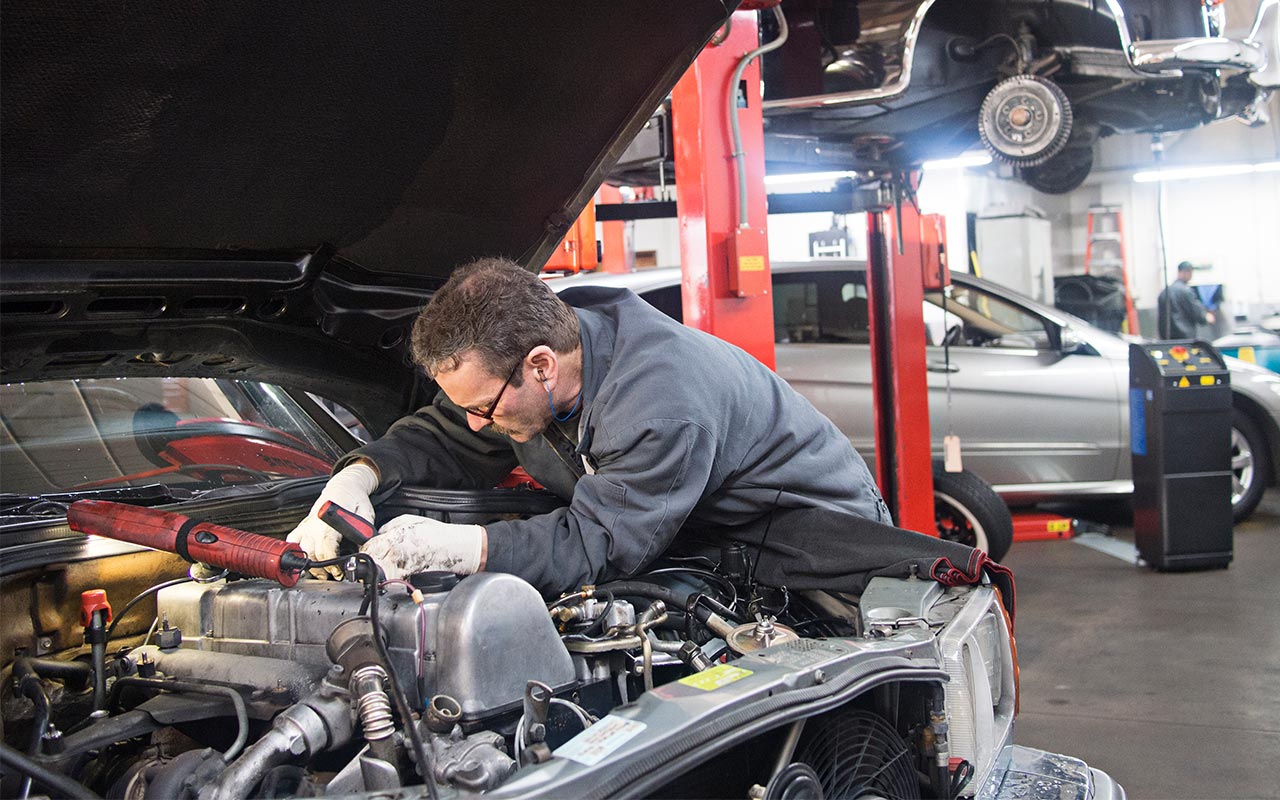
3. Automotive Repairs:
In automotive repair and fabrication, flux core welding is often chosen for its portability and ease of use. Repairing exhaust systems, fabricating brackets, or patching up body panels are common applications where flux core welding shines, offering a quick and cost-effective solution.

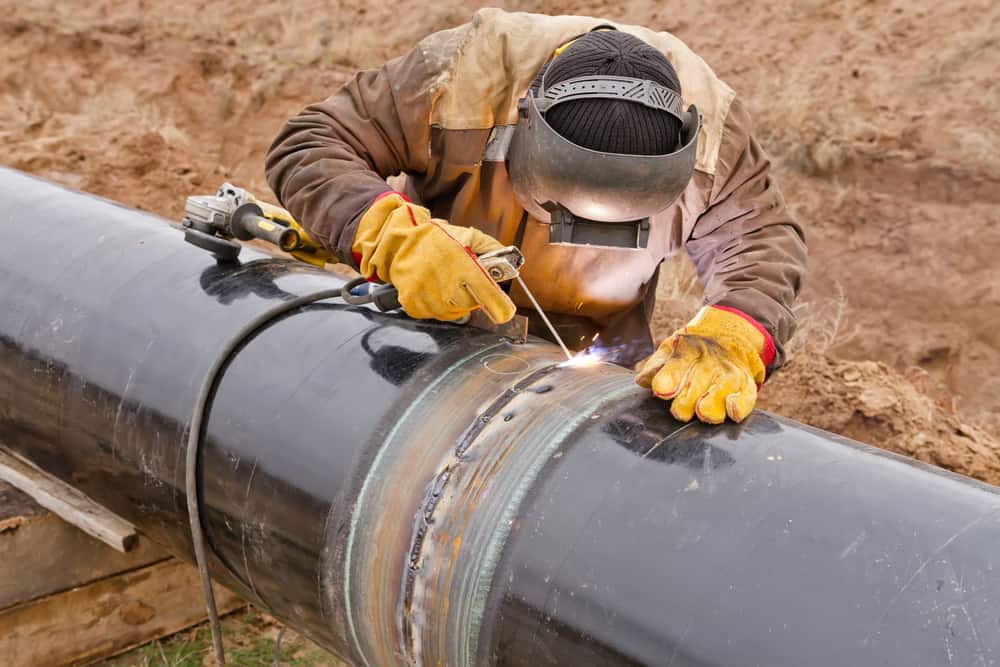
4. Pipeline Welding:
The energy sector benefits from flux core welding in the construction and maintenance of pipelines. The process’s capability to provide deep penetration is crucial for welding thick-walled pipes, ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of the pipelines that transport oil, gas, or other fluids.

5. Field Repairs and Maintenance:
Flux core welding is highly suitable for on-site repairs and maintenance tasks. Its portability and versatility make it an ideal choice for welders who need to work in diverse environments and positions. Whether it’s fixing agricultural equipment or repairing industrial machinery, flux core welding proves to be a reliable ally.

Advantages of Flux Core Welding:
1. High Deposition Rates:
Flux core welding excels in providing high deposition rates, meaning that it can lay down a substantial amount of weld metal in a short period. This is particularly advantageous in applications where efficiency and productivity are key considerations.

2. Deep Penetration:
The process’s ability to achieve deep penetration makes it well-suited for welding thick materials. This characteristic is especially beneficial in applications like structural welding and pipeline construction, where weld penetration is crucial for the overall strength of the joint.
3. All-Position Welding:
Unlike some other welding processes, flux core welding is highly versatile and can be used in all positions—flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead. This flexibility makes it an attractive choice for welders who need to work in challenging or varied conditions.

4. Portability and Convenience:
Flux core welding machines are often more portable and convenient than some other types of welding equipment. This makes them ideal for on-site repairs and construction projects where mobility is a priority.

5. Cost-Effective:
The cost-effectiveness of flux core welding is another factor contributing to its widespread use. The process eliminates the need for an external shielding gas, reducing overall operational costs. Additionally, the high deposition rates translate to faster welding, saving both time and money.

Challenges and Considerations:
While flux core welding offers numerous advantages, it is essential to consider some challenges associated with the process. One notable aspect is the production of slag, which needs to be removed after each weld. Proper cleaning is crucial to ensure the integrity of the weld and prevent potential defects. Additionally, some welders may find the process produces more spatter compared to other welding methods, requiring extra attention to post-weld cleanup.
Conclusion:
Flux core welding has undoubtedly secured its place as a versatile and efficient welding process across various industries. From its applications in construction and shipbuilding to automotive repairs and pipeline welding, flux core welding continues to prove its mettle. The advantages it offers, including high deposition rates, deep penetration capabilities, and portability, make it a preferred choice for many welders.
As technology advances, it’s likely that flux core welding will continue to evolve, addressing any challenges and further expanding its applications. Whether you are a seasoned professional or a DIY enthusiast, understanding the capabilities of flux core welding can open up new possibilities for tackling diverse welding projects with confidence and precision.
READ MORE: WHAT IS BUTTON HEAD SCREWS , AND PROPERTIES , APPLICATIONS
READ MORE: How to start a new startup business on Deepawali 2023





